What is Risk Based Inspection?
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
By
Jeffrey C. Nichols
-
How Does it Relate to Process Safety Management (PSM)?
A Risk Based Inspection (RBI) is basically a risk analysis of operational procedures. It assesses the safety risks and plant integrity that exist and further prepares it for possible inspections. The end result is a document that outlines, measures and defines organizational procedures based on standards, codes and best practices.
Per Wikipedia, "RBI is most often used in engineering industries and is predominant in the oil and gas industry. Assessed risk levels are used to develop a prioritised inspection plan. It is related to (or sometimes a part of) Risk Based Asset Management (RBAM), Risk Based Integrity Management (RBIM) and Risk Based Management (RBM). Generally, RBI is part of Risk and Reliability Management (RRM)."
Generally, RBI's are used when a company wants to change the required fregency of inspection for pressure-rate vesels. This is applicable to the mechanical integrity element of a Process Safety Management (PSM) plan and one of the top most cited elements of OSHA.
Also per Wikipedia: "Process Safety Management is an analytical tool focused on preventing releases of any substance defined as a 'highly hazardous chemical' by the Environmental Protection Agency or OSHA. PSM refers to a set of interrelated approaches to managing hazards associated with the process industries and is intended to reduce the frequency and severity of incidents resulting from releases of chemicals and other energy sources (US OSHA 1993). These standards are composed of organizational and operational procedures, design guidance, audit programs, and a host of other methods."
The U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) 1910.119 defines all 14 elements of a Process Safety Management plan. Within the 14 elements is "Mechanical Integrity of Equipment":
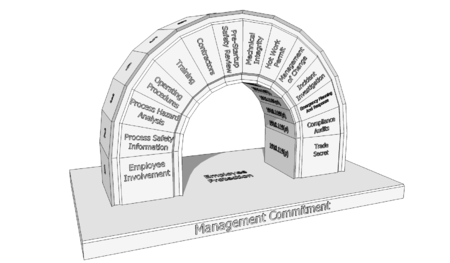 "Employers must review their maintenance programs and schedules to see if there are areas where 'breakdown' is used rather than the more preferable on-going mechanical integrity program. Equipment used to process, store, or handle highly hazardous chemicals has to be designed, constructed, installed, and maintained to minimize the risk of releases of such chemicals. This requires that a mechanical integrity program be in place to ensure the continued integrity of process equipment.
"Employers must review their maintenance programs and schedules to see if there are areas where 'breakdown' is used rather than the more preferable on-going mechanical integrity program. Equipment used to process, store, or handle highly hazardous chemicals has to be designed, constructed, installed, and maintained to minimize the risk of releases of such chemicals. This requires that a mechanical integrity program be in place to ensure the continued integrity of process equipment.
Elements of a mechanical integrity program include identifying and categorizing equipment and instrumentation, inspections and tests and their frequency; maintenance procedures; training of maintenance personnel; criteria for acceptable test results; documentation of test and inspection results; and documentation of manufacturer recommendations for equipment and instrumentation."
Where there might be a bit of overlap/similarity in RBI and PSM is in the area of mechanical integrity with regard to structural engineering. Structural engineering is an important field of engineering that deals with the integrity of objects such as plant components or structures and serves the industry by performing analytical assessments, experiments, walkdowns or numerical modeling. Some companies specialize in supporting industrial process facilities and power plants.
In plants, the structural challenges are often related to pressure, temperature and dynamic forces. An example is the seismic adequacy of piping or components under power operation. Engineers perform seismic walkdowns on a regular basis to screen for the seismic adequacy of systems. Some companies are able to follow industry guidelines such as EPRI 1019199 “Experience-Based Seismic Verification Guidelines for Piping and Tubing”. Alternatively, some have developed their own seismic screening methodology which provides an even more cost effective and conservative assessment approach. Several specialty engineers and contractors have undergone professional seismic training which also allows them to assess safety-related electrical components such as instrumentation and control components, etc.
To support plant modernization and power uprate projects, for example, there is a need to utilize all facets of structural engineering. For example, we have seen an increasing demand for vibration analyses.
Increasingly, it is imperative to effectively study the cause of the vibration and to propose solutions for elimination or mitigation. Engineers are available for on-site support which includes measurement, troubleshooting and root cause analysis in a team setting together with the client.
Proper application of structural engineering expertise can help mitigate issues by ensuring that the plant and components are properly engineered. This will avoid machinery breakdown and costly plant outages. The goal is to support customers to achieve a safer and more efficient work environment along with enhanced plant durability.
Thus, for several aspects of RBI and PSM, an engineering firm with testing labs are ideal in providing a one-stop-resource for structural engineering issues including analyzing a problem, engineering a solution, verification, as well as oversight of fabrication and installation, as required.
What else?
Also within the PSM Elements defined by OSHA is Process Hazards Analysis (PHA) - a systematic evaluation of the hazards involved in the process. PHAs are required for initiation of a process and at least once every five years after that. It is important to address normal operating conditions as well as start-up, normal shut down and emergency shutdown procedures during the PHA. The PHA team should be multi-disciplinary, including operations, engineering and maintenance. To properly conduct a PHA, the process safety information (PSI) must be as complete as possible.
 In response to continued rapid growth in safety needs for the chemical, nuclear and other industries, a few process safety engineering labs offer a complete range of Risk Management Services (RMS) such as Combustible Dust Hazard Assessment (DHA) Explosion and Fire Hazard Evaluation, Process Hazard Analysis (PHA), Hazard Identification Risk Analysis, Consequence Analysis, Safer Process Scale-up, Process Safety Management (PSM) Program Development, and Relief System Design Review to name a few.
In response to continued rapid growth in safety needs for the chemical, nuclear and other industries, a few process safety engineering labs offer a complete range of Risk Management Services (RMS) such as Combustible Dust Hazard Assessment (DHA) Explosion and Fire Hazard Evaluation, Process Hazard Analysis (PHA), Hazard Identification Risk Analysis, Consequence Analysis, Safer Process Scale-up, Process Safety Management (PSM) Program Development, and Relief System Design Review to name a few.
Benefits to having RMS to help an RBI are:
Combustible Dust Hazard Analysis (DHA) Explosion and Fire Hazard Evaluation
Experts provide onsite Combustible Dust Hazard Assessments (DHAs), Process Hazard Analyses (PHAs), OSHA Combustible Dust NEP compliance support, training and other services related to characterizing, preventing and mitigating combustible dust explosion and fire hazards. An onsite assessment provides an experienced engineer to visit a facility, evaluate its compliance with relevant national, local and industry standards and provide recommendations for risk reduction. Additional services can include deflagration vent sizing calculations, desktop reviews, equipment selection guidance, training of personnel on combustible dust hazards as well as development of process safety programs to address these issues.
Process Hazard Analysis (PHA)
Process safety professionals can provide PHA services including PHA auditing / review, revalidating PHAs and facilition. Some perform PHAs for compliance to OSHA PSM requirements as well as combustible dust related PHAs for compliance per National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) guidelines: NFPA 654, NFPA 664 and NFPA 484.
Some perform PHAs for compliance to OSHA PSM requirements as well as combustible dust related PHAs for compliance per National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) guidelines: NFPA 654, NFPA 664 and NFPA 484.
Look for an organization that can provide a full range of PHA services, using a variety of techniques including, hazard and operability (HAZOP) analysis, what-if, checklists, failure modes and effects analysis (FMEA) as well as quantitative risk assessments such as layer of protection analysis (LOPA).
Hazard Identification & Risk Analysis
Consulting services to identify hazards related to the handling or storage of flammable and combustible liquids and gases, combustible dust and reactive chemicals may be needed for your organization. Extensive testing experience provides the ability to identify potentially hazardous conditions that may not be readily discernable.
Consequence Analysis
Experts can evaluate the effect of various process upset scenarios including fire and explosions, vessel overpressure scenarios, chemical reactivity concerns, vapor cloud dispersions and chemical releases. Computer models may be used in conjunction with appropriate data to determine the effects. The benefit or risk reduction of safeguards or mitigation strategies can also be evaluated.
Fire Protection Engineering
Provides life safety and fire protection consulting, engineering, and design services to architects, owners and developers, construction teams and facility operators. Helps clients to understand and achieve essential life safety goals like complying with codes, meeting egress requirements, choosing sustainable fire protection systems, analyzing hazards, and preparing for and responding to emergencies. Why? Risk mitigation; help to lower design, construction, and operating budgets; and ensure enhanced safety for end users. May include:
Safer Process Scale-Up
Also seek services for safer scale-up of batch, semi-batch and continuous processes. Consultation is available for process development groups involved in the scale-up of chemical processes throughout the development cycle. Areas of expertise may include the following topics:
Process Safety Management (PSM) Program Development and Support
Relief System Design Review
Look for experts in the Design Institute of Emergency Relief Systems (DIERS) research project team. Those who participate in the DIERS users group and contribute to developments in relief system design technology provide testing experience and the unique capability to consult on this topic with proficiency. Your organization may need:
Training!
Professionals are happy to train your staff in the understanding of technical issues, process safety programs or audits, regulations and more. Look for organizations that perform process safety audits as part of a comprehensive hazards analysis and can work with you to make sure your staff is supplied with training needs in many ways including:
Level I - Gap Analysis
Level II - Training & Consulting
Level III - Program Development and Implementation
Partial List of Services To Seek in an Engineering and Testing Lab:
Because of the unique work we do in the fields of safety for chemical process, nuclear and industrial areas, we are constantly able to cross examine and engineer, test and consult with new applications and capability. For more discussion or information, please contact AnnMarie Fauske, afauske@fauske.com, 630-887-5313. www.fauske.com
By AnnMarie Fauske, Customer Outreach & Digital Media Manager
Posted by AnnMarie Fauske on Thu, Mar 23, 2017 @ 12 37 PM
A Risk Based Inspection (RBI) is basically a risk analysis of operational procedures. It assesses the safety risks and plant integrity that exist and further prepares it for possible inspections. The end result is a document that outlines, measures and defines organizational procedures based on standards, codes and best practices.

Per Wikipedia, "RBI is most often used in engineering industries and is predominant in the oil and gas industry. Assessed risk levels are used to develop a prioritised inspection plan. It is related to (or sometimes a part of) Risk Based Asset Management (RBAM), Risk Based Integrity Management (RBIM) and Risk Based Management (RBM). Generally, RBI is part of Risk and Reliability Management (RRM)."
Generally, RBI's are used when a company wants to change the required fregency of inspection for pressure-rate vesels. This is applicable to the mechanical integrity element of a Process Safety Management (PSM) plan and one of the top most cited elements of OSHA.
Also per Wikipedia: "Process Safety Management is an analytical tool focused on preventing releases of any substance defined as a 'highly hazardous chemical' by the Environmental Protection Agency or OSHA. PSM refers to a set of interrelated approaches to managing hazards associated with the process industries and is intended to reduce the frequency and severity of incidents resulting from releases of chemicals and other energy sources (US OSHA 1993). These standards are composed of organizational and operational procedures, design guidance, audit programs, and a host of other methods."
The U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) 1910.119 defines all 14 elements of a Process Safety Management plan. Within the 14 elements is "Mechanical Integrity of Equipment":
 "Employers must review their maintenance programs and schedules to see if there are areas where 'breakdown' is used rather than the more preferable on-going mechanical integrity program. Equipment used to process, store, or handle highly hazardous chemicals has to be designed, constructed, installed, and maintained to minimize the risk of releases of such chemicals. This requires that a mechanical integrity program be in place to ensure the continued integrity of process equipment.
"Employers must review their maintenance programs and schedules to see if there are areas where 'breakdown' is used rather than the more preferable on-going mechanical integrity program. Equipment used to process, store, or handle highly hazardous chemicals has to be designed, constructed, installed, and maintained to minimize the risk of releases of such chemicals. This requires that a mechanical integrity program be in place to ensure the continued integrity of process equipment.Elements of a mechanical integrity program include identifying and categorizing equipment and instrumentation, inspections and tests and their frequency; maintenance procedures; training of maintenance personnel; criteria for acceptable test results; documentation of test and inspection results; and documentation of manufacturer recommendations for equipment and instrumentation."
Where there might be a bit of overlap/similarity in RBI and PSM is in the area of mechanical integrity with regard to structural engineering. Structural engineering is an important field of engineering that deals with the integrity of objects such as plant components or structures and serves the industry by performing analytical assessments, experiments, walkdowns or numerical modeling. Some companies specialize in supporting industrial process facilities and power plants.
In plants, the structural challenges are often related to pressure, temperature and dynamic forces. An example is the seismic adequacy of piping or components under power operation. Engineers perform seismic walkdowns on a regular basis to screen for the seismic adequacy of systems. Some companies are able to follow industry guidelines such as EPRI 1019199 “Experience-Based Seismic Verification Guidelines for Piping and Tubing”. Alternatively, some have developed their own seismic screening methodology which provides an even more cost effective and conservative assessment approach. Several specialty engineers and contractors have undergone professional seismic training which also allows them to assess safety-related electrical components such as instrumentation and control components, etc.
To support plant modernization and power uprate projects, for example, there is a need to utilize all facets of structural engineering. For example, we have seen an increasing demand for vibration analyses.
Increasingly, it is imperative to effectively study the cause of the vibration and to propose solutions for elimination or mitigation. Engineers are available for on-site support which includes measurement, troubleshooting and root cause analysis in a team setting together with the client.
Proper application of structural engineering expertise can help mitigate issues by ensuring that the plant and components are properly engineered. This will avoid machinery breakdown and costly plant outages. The goal is to support customers to achieve a safer and more efficient work environment along with enhanced plant durability.
Thus, for several aspects of RBI and PSM, an engineering firm with testing labs are ideal in providing a one-stop-resource for structural engineering issues including analyzing a problem, engineering a solution, verification, as well as oversight of fabrication and installation, as required.
What else?
Also within the PSM Elements defined by OSHA is Process Hazards Analysis (PHA) - a systematic evaluation of the hazards involved in the process. PHAs are required for initiation of a process and at least once every five years after that. It is important to address normal operating conditions as well as start-up, normal shut down and emergency shutdown procedures during the PHA. The PHA team should be multi-disciplinary, including operations, engineering and maintenance. To properly conduct a PHA, the process safety information (PSI) must be as complete as possible.
 In response to continued rapid growth in safety needs for the chemical, nuclear and other industries, a few process safety engineering labs offer a complete range of Risk Management Services (RMS) such as Combustible Dust Hazard Assessment (DHA) Explosion and Fire Hazard Evaluation, Process Hazard Analysis (PHA), Hazard Identification Risk Analysis, Consequence Analysis, Safer Process Scale-up, Process Safety Management (PSM) Program Development, and Relief System Design Review to name a few.
In response to continued rapid growth in safety needs for the chemical, nuclear and other industries, a few process safety engineering labs offer a complete range of Risk Management Services (RMS) such as Combustible Dust Hazard Assessment (DHA) Explosion and Fire Hazard Evaluation, Process Hazard Analysis (PHA), Hazard Identification Risk Analysis, Consequence Analysis, Safer Process Scale-up, Process Safety Management (PSM) Program Development, and Relief System Design Review to name a few.Benefits to having RMS to help an RBI are:
- Understand and address hazards that pose the highest level of risk to your process facility
- Ensure compliance with relevant national, local and industry standards
- Implement best engineering practices
- Reduce overall level of risk
- Increase productivity and employee morale
- Make organization more competitive
- Decrease insurance premiums
Combustible Dust Hazard Analysis (DHA) Explosion and Fire Hazard Evaluation
Experts provide onsite Combustible Dust Hazard Assessments (DHAs), Process Hazard Analyses (PHAs), OSHA Combustible Dust NEP compliance support, training and other services related to characterizing, preventing and mitigating combustible dust explosion and fire hazards. An onsite assessment provides an experienced engineer to visit a facility, evaluate its compliance with relevant national, local and industry standards and provide recommendations for risk reduction. Additional services can include deflagration vent sizing calculations, desktop reviews, equipment selection guidance, training of personnel on combustible dust hazards as well as development of process safety programs to address these issues.
Process Hazard Analysis (PHA)
Process safety professionals can provide PHA services including PHA auditing / review, revalidating PHAs and facilition.
 Some perform PHAs for compliance to OSHA PSM requirements as well as combustible dust related PHAs for compliance per National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) guidelines: NFPA 654, NFPA 664 and NFPA 484.
Some perform PHAs for compliance to OSHA PSM requirements as well as combustible dust related PHAs for compliance per National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) guidelines: NFPA 654, NFPA 664 and NFPA 484.Look for an organization that can provide a full range of PHA services, using a variety of techniques including, hazard and operability (HAZOP) analysis, what-if, checklists, failure modes and effects analysis (FMEA) as well as quantitative risk assessments such as layer of protection analysis (LOPA).
Hazard Identification & Risk Analysis
Consulting services to identify hazards related to the handling or storage of flammable and combustible liquids and gases, combustible dust and reactive chemicals may be needed for your organization. Extensive testing experience provides the ability to identify potentially hazardous conditions that may not be readily discernable.
Consequence Analysis
Experts can evaluate the effect of various process upset scenarios including fire and explosions, vessel overpressure scenarios, chemical reactivity concerns, vapor cloud dispersions and chemical releases. Computer models may be used in conjunction with appropriate data to determine the effects. The benefit or risk reduction of safeguards or mitigation strategies can also be evaluated.
Fire Protection Engineering
Provides life safety and fire protection consulting, engineering, and design services to architects, owners and developers, construction teams and facility operators. Helps clients to understand and achieve essential life safety goals like complying with codes, meeting egress requirements, choosing sustainable fire protection systems, analyzing hazards, and preparing for and responding to emergencies. Why? Risk mitigation; help to lower design, construction, and operating budgets; and ensure enhanced safety for end users. May include:
- Building and fire code consulting
- Means of egress evaluation
- Plan review
- Commissioning and construction management services
- Fire modeling
- Explosion modeling
- Dispersion modeling
- Quantitative risk analysis
Safer Process Scale-Up
Also seek services for safer scale-up of batch, semi-batch and continuous processes. Consultation is available for process development groups involved in the scale-up of chemical processes throughout the development cycle. Areas of expertise may include the following topics:
- Onsite or desktop review
- Determine critical process parameters to avoid or mitigate unwanted reactivity
- Development of customized scale-up program designed for safer operation at various stages
- Perform calorimetry testing to characterize desired and undesired reactions
- Identify safe operating limits for temperature, pressure and other safety-critical parameters
- Emergency relief design calculations for pilot plant, kilo lab and commercial scale equipment
- Independent safety assessment
Process Safety Management (PSM) Program Development and Support
Seek a review or develop a process safety program to support chemical manufacturing facilities or development programs. This can be performed for facilities including a kilo lab, pilot plant, medium scale and commercial scale plants. Services/needs might include:
- Auditing, reporting and presenting
- Gap assessment to identify and prioritize needs
- Process validation
- Safe scale-up guidance
- Development report documentation
- Consulting on process safety issues for change control (management of change)
Relief System Design Review
Look for experts in the Design Institute of Emergency Relief Systems (DIERS) research project team. Those who participate in the DIERS users group and contribute to developments in relief system design technology provide testing experience and the unique capability to consult on this topic with proficiency. Your organization may need:

- Third party review of existing relief system design
- Provide cost-effective solutions if existing relief system design is not adequate
- Ensure current design basis is appropriate and credible
- Develop / review pressure relief guidelines
- Specialists in effluent control for two-phase flow systems
Training!
Professionals are happy to train your staff in the understanding of technical issues, process safety programs or audits, regulations and more. Look for organizations that perform process safety audits as part of a comprehensive hazards analysis and can work with you to make sure your staff is supplied with training needs in many ways including:
Level I - Gap Analysis
Level II - Training & Consulting
Level III - Program Development and Implementation
Partial List of Services To Seek in an Engineering and Testing Lab:
- Reviews and upgrades of all your safety process systems and regulatory requirements
- VPP Consulting
- Audits, reviews, and upgrades of all your Operating, Safety, and Maintenance Procedures
- Training program evaluations for both completeness and effectiveness (from technical skills to professional development) and upgrades where needed
- Reviews and upgrades of your program elements such as Employee Participation and Process Safety Information for effectiveness and completeness
- Work process effectiveness evaluations and upgrades
- Overall organizational development (e.g., motivation, work processes)
- Stress reduction
- Evaluations of the effectiveness of communication
Because of the unique work we do in the fields of safety for chemical process, nuclear and industrial areas, we are constantly able to cross examine and engineer, test and consult with new applications and capability. For more discussion or information, please contact AnnMarie Fauske, afauske@fauske.com, 630-887-5313. www.fauske.com
By AnnMarie Fauske, Customer Outreach & Digital Media Manager
Comments
Post a Comment